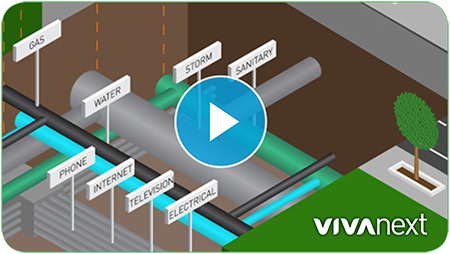
The importance of upgrading Canada’s infrastructure is everywhere in the news these days. Infrastructure includes everything from bridges to roads and transit, to utilities such as hydro lines, sewers and water mains. Each vivaNext project includes improvements to infrastructure and utilities, leaving a lasting legacy for residents and businesses. One of the most important pieces of infrastructure is a water main – bringing fresh water to your mealtime prep, your kids’ bath tub and even your local swimming pool. In Richmond Hill, the residents and businesses connecting to Yonge Street are getting a new, modern water main to prepare for future growth.
Although to some people it might not seem very glamorous, an important example of a major infrastructure improvement is the replacement of the Richmond Hill water main, which we’re doing as part of the vivaNext Yonge Street rapidway project. This work will replace 3.7 kilometres of water main along Yonge Street from just south of Garden Avenue [north of Highway 407] to Major Mackenzie Drive. The water main, which supplies water to the adjacent residents, is owned and maintained by the Town of Richmond Hill, with construction done by the vivaNext Design Build contractor.
Water main replacements, especially in busy thoroughfares like Yonge Street, require complex planning for design, staging and construction. As with all our work, we need to find a balance between a number of competing priorities. One priority is to maintain service to households and businesses who depend on the water main. Another priority is to get the work done in a way that minimizes disruption to traffic. And, as always, we need to plan the design and construction in a way that gets the most value for money, including future maintenance costs.
To avoid existing underground utilities and simplify construction, we’ll relocate the water main to run under the traffic lanes on Yonge Street. We also want to avoid locating it under the new planters that will be built along the sidewalk, in the event that future maintenance on the water main is needed.
Replacement water mains are generally located as close as possible to the original water main, to preserve existing connections to residences and businesses. As a result, construction proceeds more slowly to avoid any damage during excavation to the existing water main, which stays in use until the new one is ready for service.
To minimize disruption to traffic, workers will be building the new water main from inside a trench box, which significantly reduces the amount of space needed to carry out the construction compared to regular excavation. The benefit of constructing in less space is that fewer lane closures are needed during construction, which is critical on Yonge Street.
However, trench box construction has to move more slowly. The rigid trench box also makes it more challenging to work around conflicts with other buried infrastructure. From time to time we can expect progress to slow down while crews get around other underground utilities. Construction will be followed by a lengthy process of pressurizing, cleaning and testing, all to meet very strict government standards.
Once the new water main is ready to go, a new connection to each address along the main route will need to be made, along with additional connections to other water mains at intersections. Individual addresses are relatively straightforward to reconnect, but businesses and multi-unit residential buildings take longer, with connections to larger pipes and fire lines. This process of disconnection and reconnection will be planned ahead, with communication with each residence and business to minimize disruption.
We’re excited that the community is going to be getting a new water main, built to the most modern standards. Our team is working with the community during construction to help minimize any impacts to parking and driveways. And we’ll make sure there’s lots of clear signage to help guide you through construction areas.
It’s a huge project, and it’s going to be pretty messy out there for a while. But long term, it’s great news for the residents of Richmond Hill that this huge investment is being made in infrastructure. We hope this helps explain what the crews are doing out there, and how it makes a difference to the community. For more information on ongoing work be sure to sign up for email updates, and follow us on Twitter.