Property ownership and development are generally straightforward concepts: people or businesses own land, including any assets that are built on that land, and only they can decide when and if any improvements are to be made.
But what happens when the property is located underground, and the improvements are being made by someone other than the property owner? Welcome to the murky and confusing world of underground infrastructure, where ownership and decision-making are much more complex than above ground.
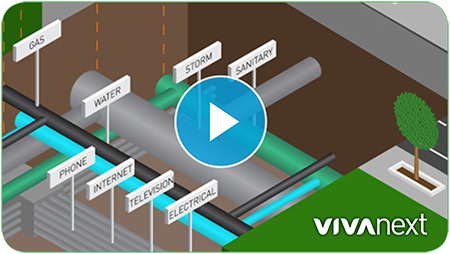
Underground infrastructure, which includes gas and power lines, telecommunications, watermains and sewers, is always owned by either a private company or the municipality. But generally utilities are located under roads or sidewalks, or on private property; utility companies typically do not own the land where their utilities are located.
In most cases underground infrastructure is located in the “public right-of-way”, including roads, sidewalks and boulevards. If a utility company wants to make a change to their own infrastructure, such as making a repair or increasing capacity, they need to get municipal approval before any work can be done. This “municipal consent” process is set out in legislation, and ensures municipalities can control and coordinate utility work on public lands or roads. This is critical, especially when utility work requires road closures or detours or will have some other impact on the public.
Municipalities also can set restrictions on when and how utilities can access their own infrastructure, to minimize impacts on the public and protect the municipality’s own infrastructure. For example, a municipality might impose a moratorium on changes to private infrastructure on newly built or repaired streets, so that new asphalt isn’t dug up.
In all cases, our projects spend a lot of time coordinating with utility companies to resolve any conflicts between the rapidway and streetscape elements we’re building, and the multiple utilities using the same space. In many cases, utilities can co-locate, for example telecommunications may share a common duct bank, and be buried next to hydro. Designs for all relocated utilities have to work with our vivaNext design, and in some cases where space is limited, working through the design process to fit in all the elements can be extremely challenging. Municipalities also have views on where they want elements located; the Region avoids locating utilities in their roadway, whereas local municipalities prefer to keep utilities away from the planters.
Once the design is established, a schedule is worked out with the Region or municipalities, specifying how long the utility work will take. Utilities are given a specified amount of time to close lanes as part of the final permit; even if the work is next to the road, lanes often need to be closed to give workers room to work safely. Our design-builders will coordinate construction work with the utility relocations, since only one activity can be carried out at a time in any given place.
The last but very important part of this complicated process is reducing the disruption for nearby residents and businesses. Once the design and municipal consent is complete, the utility and vivaNext community liaison team work with property owners to discuss access to properties while work is underway.
A lot of moving parts need to be coordinated and resolved before any underground infrastructure gets moved, but our teams are committed to coordinating these efforts with everyone’s best interests in mind.